Abstract
Research Article
Self-care practice and associated factors among type 2 adult diabetic patients on follow up clinic of Dessie referral hospital, Northeast Ethiopia
Sisay Gedamu Addis*, Sewunet Ademe Kassahun, Samuel Anteneh Ayele, Abebe Dires Nega and Kirubel Dagnaw Tegegne
Published: 07 June, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 031-037
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a common health problem in the world and Africa including Ethiopia. Its complication is the major cause of morbidity and mortality of people due to improper self-care practice.
Objective: To assess self-care practices and associated factors among type 2 adult diabetic patients on follow-up clinic of Dessie referral hospital, Ethiopia.
Method: Institutional based cross sectional study was conducted. Total of 278 type 2 diabetic patients was selected by systematic random sampling technique and data was collected by interviewer administered pretested questionnaire. Epidata 3.1 and SPSS version 23 software were used for data entry and analysis, respectively. In bivariate analysis, variables having a p - value of < 0.2 were entered to multivariate analysis model and statistical significance was declared at p - value of < 0.05 and 95% confidence interval.
Results: The response rate was 269 (96.76%) of the total 278 participants. Among the respondents 150(55.8%) had good diabetic self-care practice. This study showed that primary school education level (AOR=2.592, 95%CI=1.104-6.087, p = 0.029), secondary school education level (AOR=3.873, 95%CI=1.325-11.323, p = 0.013), college/university graduate (AOR=3.030, 95%CI=1.276-7.197, 0.012), attended diabetic education regularly (AOR=2.981, 95%CI=1.050-8.462, p = 0.040), member of diabetic association (AOR=3.496, 95%CI=1.440-8.483, p = 0.006) and having glucometer at home (AOR=2.634, 95%CI=1.357-5.111, p = 0.004) were significantly associated with diabetes self-care practice.
Conclusion: Nearly half of diabetic patients had poor self care practice. Hence, there is a need to improve diabetic self-care practice. Attention should be given by policy makers, Dessie referral hospital, health care professionals, diabetic associations and researchers.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001034 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Self-care practice; Associated factors; Type 2 diabetic patients; Adult; Dessie referral hospital; Northeast Ethiopia
References
- Kerner W, Brückel J. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2014; 122: 384-386. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25014088/
- Lichtman SW, Pisarska K, Berman ER, Pestone M, Dowling H, et al. Discrepancy between self-reported and actual caloric intake and exercise in obese subjects. New Eng J Med. 1992; 327: 1893-1898. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1454084/
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42: S13-S28. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30559228/
- Anderson RM, Funnell MM, Butler PM, Arnold MS, Fitzgerald JT, et al. Patient empowerment: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 1995; 18: 943-949. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7555554/
- Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: a systematic review. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28: 1510-1517. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15920083/
- Garcia-Perez LE, Álvarez M, Dilla T, Gil-Guillén V, Orozco-Beltrán D. Adherence to therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2013; 4: 175-194. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23990497/
- Coyle ME, Francis K, Chapman Y. Self-management activities in diabetes care: a systematic review. Australian Health Rev. 2013; 37: 513-522. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24018058/
- Chen L, Chuang LM, Chang CH, Wang CS, Wang IC, Chung Y, et al. Evaluating self-management behaviors of diabetic patients in a telehealthcare program: longitudinal study over 18 months. J Med Internet Res. 2013; 15: e266. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24323283/
- Padma K, Bele SD, Bodhare TN, Valsangkar S. Evaluation of knowledge and self-care practices in diabetic patients and their role in disease management. National J Commun Med. 2012; 3: 3-6.
- Shrivastava SR, Shrivastava PS, Ramasamy J. Role of self-care in management of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metabo Disord. 2013; 12: 14. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23497559/
- Okolie VU, Ehiemere OI, Peace IN, Ngozi K-II. Knowledge of diabetes management and control by diabetic patients at Federal Medical Center Umuahia Abia State, Nigeria. Int J Med Medical Sci. 2009; 1: 353-358.
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Practice. 2010; 87: 4-14. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19896746/
- Nathan DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. New Eng J Med. 1993; 328: 1676-1685. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8487827/
- World Health Organization. Global report on diabetes. 2016.
- Breitscheidel L, Stamenitis S, Dippel FW, Schöffski O. Economic impact of compliance to treatment with antidiabetes medication in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review paper. J Med Econ. 2010; 13: 8-15. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19947905/
- Abdulameer SA, Sulaiman SAS, Hassali MAA, Subramaniam K, Sahib MN. Osteoporosis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: what do we know, and what we can do? Patient Prefer Adherence. 2012; 6: 435-448. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22791981/
- Loganathan A, John K. Economic burden of diabetes in people living with the disease; a field study. J Diabetol. 2013; 4: 5.
- Çetin EN, Zencir M, Fenkçi S, Akın F, Yıldırım C. Assessment of awareness of diabetic retinopathy and utilization of eye care services among Turkish diabetic patients. Primary Care Diabetes. 2013; 7: 297-302. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23639610/
- Addisu Y, Eshete A, Hailu E. Assessment of diabetic patient perception on diabetic disease and self-care practice in Dilla University Referral Hospital, South Ethiopia. J Metabolic Synd. 2014; 3: 2167-0943.1000166.
- Bonger Z, Shiferaw S, Tariku EZ. Adherence to diabetic self-care practices and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2018; 12: 963-970. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29922042/
- Chali SW, Salih MH, Abate AT. Self-care practice and associated factors among Diabetes Mellitus patients on follow up in Benishangul Gumuz Regional State Public Hospitals, Western Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes. 2018; 11: 833. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30477553/
- Abate TW, Tareke M, Tirfie M. Self-care practices and associated factors among diabetes patients attending the outpatient department in Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2018; 11: 800. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30409148/
- Aschalew AY, Yitayal M, Minyihun A, Bisetegn TA. Self-care practice and associated factors among patients with diabetes mellitus on follow up at University of Gondar Referral Hospital, Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2019; 12: 591. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31533833/
- Berhe KK, Demissie A, Kahsay AB, Gebru HB. Diabetes self care practices and associated factors among type 2 diabetic patients in Tikur Anbessa specialized hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia-a cross sectional study. Int J Pharmaceut Sci Res. 2012; 3: 4219.
- Upadhyay DK, Palaian S, Shankar PR, Mishra P, Pokhara N. Knowledge, attitude and practice about diabetes among diabetes patients in Western Nepal. Rawal Med J. 2008; 33: 8-11.
- Feleke SA, Alemayehu CM, Adane HT, Onigbinde A, Akindoyi O, Faremi F. Assessment of the level and associated factors with knowledge and practice of diabetes mellitus among diabetic patients attending at FelegeHiwot hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Clin Med Res. 2013; 2: 110.
- Given CW, Given BA, Gallin RS, Condon JW. Development of scales to measure beliefs of diabetic patients. Res Nurs Health. 1983; 6: 127-141. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6556699/
- Adejoh SO. Diabetes knowledge, health belief, and diabetes management among the Igala, Nigeria. Sage Open. 2014; 4: 2158244014539966.
- Tegegne GT, Shiferaw A, Gelaw BK, Defersha AD, Linjesa MAW, et al. Glycemic control and self-care practice among ambulatory diabetic patients in ambo general hospital, West Showa, Ethiopia. Glob J Med Res. 2014; 14: 26-36.
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2014. Diabetes care. 2014; 37: S14-80. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24357209/
- Ayele K, Tesfa B, Abebe L, Tilahun T, Girma E. Self care behavior among patients with diabetes in Harari, Eastern Ethiopia: the health belief model perspective. PloS One. 2012; 7: e35515. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22530039/
- Mariye T, Tasew H, Teklay G, Gerensea H, Daba W. Magnitude of diabetes self-care practice and associated factors among type two adult diabetic patients following at public Hospitals in central zone, Tigray Region, Ethiopia, 2017. BMC Res Notes. 2018; 11: 380. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29895315/
- Amente T, Belachew T, Hailu E, Berhanu N. Self care practice and its predictors among adults with diabetes mellitus on follow up at Nekemte hospital diabetic clinic, West Ethiopia. World J Med Med Sci. 2014; 2: 1-16.
- Suguna A, Magal A, Stany A, Sulekha T, Prethesh K. Evaluation of self-care practices among diabetic patients in a rural area of Bangalore district, India. Int J Curr Res Aca Rev. 2015; 3: 415-22.
- Li N, Yang X, Deng Y, Gu H, Ren X, et al. Diabetes self-management and its association with diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. [Zhonghua yan ke za zhi] Chinese J Ophthalmol. 2013; 49: 500-506. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24119962/
- Tan S, Juliana S, Sakinah H. Dietary compliance and its association with glycemic control among poorly controlled type 2 diabetic outpatients in Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia. Malaysian J Nutrit. 2011; 17; 287-299. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22655451/
Figures:
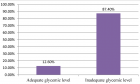
Figure 1
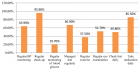
Figure 2
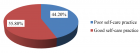
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
Knowledge, attitude, practice and associated factors towards nursing care documentation among nurses in West Gojjam Zone public hospitals, Amhara Ethiopia, 2018Atsedemariam Andualem*,Tarekegn Asmamaw,Mezinew Sintayehu,Tiliksew Liknaw,Afework Edmealem,Bekalu Bewuket,Mihretie Gedfew. Knowledge, attitude, practice and associated factors towards nursing care documentation among nurses in West Gojjam Zone public hospitals, Amhara Ethiopia, 2018. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001010; 3: 001-013
-
Knowledge and views about coordinated individual planning from the perspective of active older adultsIngela Jobe,Asa Engstrom,Birgitta Lindberg*. Knowledge and views about coordinated individual planning from the perspective of active older adults. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001012; 3: 017-026
-
Patients’ satisfaction and associated factors towards nursing care in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast EthiopiaAfework Edmealem*,Yabebal Asfaw,Sewunet Ademe,Belachew Tegegne. Patients’ satisfaction and associated factors towards nursing care in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001018; 3: 053-058
-
Health care workers knowledge, attitude and practice towards hospital acquired infection prevention at Dessie referral hospital, Northeast EthiopiaHailemariam Gezie,Emebet Leta,Fikrte Admasu,Sisay Gedamu*,Abebe Dires,Debrnesh Goshiye. Health care workers knowledge, attitude and practice towards hospital acquired infection prevention at Dessie referral hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001019; 3: 059-063
-
Influence of adverse socio-emotional risk factors on the physical and mental health needs of children and young people in public care of a South-West England local authorityMichael O Ogundele*. Influence of adverse socio-emotional risk factors on the physical and mental health needs of children and young people in public care of a South-West England local authority. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001021; 4: 001-009
-
Knowledge and attitude of workers towards HIV post-exposure prophylaxis and exposure of staffs to sharp injuries in Dessie Referral Hospital: 2020; A cross sectional studySewunet Ademe*,Mekia Mohammed,Afework Edmealem. Knowledge and attitude of workers towards HIV post-exposure prophylaxis and exposure of staffs to sharp injuries in Dessie Referral Hospital: 2020; A cross sectional study. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001025; 4: 032-038
-
Self-care practice and associated factors among type 2 adult diabetic patients on follow up clinic of Dessie referral hospital, Northeast EthiopiaSisay Gedamu Addis*,Sewunet Ademe Kassahun,Samuel Anteneh Ayele,Abebe Dires Nega,Kirubel Dagnaw Tegegne. Self-care practice and associated factors among type 2 adult diabetic patients on follow up clinic of Dessie referral hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001034; 5: 031-037
-
Sleep quality and associated factors among patients with chronic illness at South Wollo Zone Public Hospitals, Northeast EthiopiaAfework Edmealem*,Sewunet Ademe,Atsedemariam Andualem . Sleep quality and associated factors among patients with chronic illness at South Wollo Zone Public Hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001036; 5: 043-050
-
Knowledge and self-reported practice of insulin injection device disposal and associated factors among diabetes patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A cross-sectional studyAynalem Loha,Fekadu Aga,Amanuel Fanta*. Knowledge and self-reported practice of insulin injection device disposal and associated factors among diabetes patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001042; 6: 020-026
-
Medication Compliance and Affecting Factors in Elderly Type 2 Diabetic Patients in TurkeyPapatya Karakurt*,Mesut Inci. Medication Compliance and Affecting Factors in Elderly Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Turkey. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001057; 8: 044-050
Recently Viewed
-
Strengthening Healthcare Delivery in the Democratic Republic of Congo through Adequate Nursing WorkforceMin Kyung Shin, Tshibambe N Tshimbombu*. Strengthening Healthcare Delivery in the Democratic Republic of Congo through Adequate Nursing Workforce. Clin J Nurs Care Pract. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001051; 8: 007-010
-
Chemical constituents and biological activities of Artocarpus heterophyllus lam (Jackfruit): A reviewSibi G*,Pranay Raja Bhad,Meeneri Vilas Bobde. Chemical constituents and biological activities of Artocarpus heterophyllus lam (Jackfruit): A review. Int J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcmbt.1001019; 4: 005-009
-
The clinicopathological correlates of Cystoisosporiasis in immunocompetent, immunocompromised and HIV-infected/AIDS patients, but neglected in SARS-COV-2/COVID-19 patients?Chrysanthus Chukwuma Sr*. The clinicopathological correlates of Cystoisosporiasis in immunocompetent, immunocompromised and HIV-infected/AIDS patients, but neglected in SARS-COV-2/COVID-19 patients?. Int J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcmbt.1001018; 4: 001-004
-
Explicating the presentations of Acanthamoeba keratitis with special concern in the COVID-19 pandemic ambientChrysanthus Chukwuma Sr*. Explicating the presentations of Acanthamoeba keratitis with special concern in the COVID-19 pandemic ambient. Int J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcmbt.1001020; 4: 010-015
-
Coronavirus COVID-19 surface properties: Electrical charges statusLuisetto M*,Tarro G,Khaled Edbey,Farhan Ahmad Khan,Yesvi AR,Nili BA,Fiazza C,Mashori GR,President, IMA Academy, Italy. Coronavirus COVID-19 surface properties: Electrical charges status. Int J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcmbt.1001021; 4: 016-027
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."